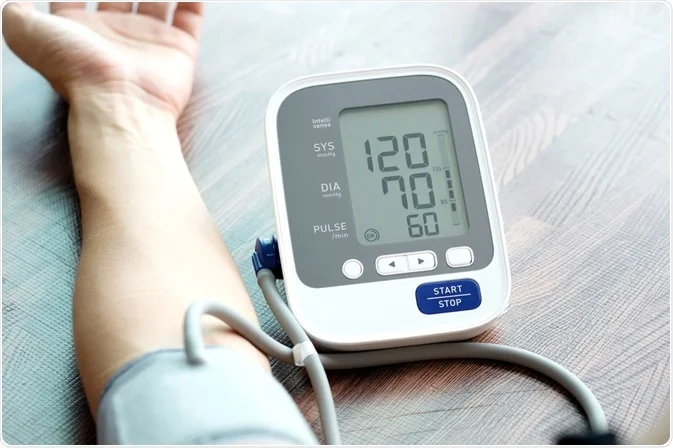
How does a Blood Pressure Measuring Machine Works?
Blood pressure is a crucial health indicator that provides important information about the function of the heart and circulatory system. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health problem that increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health complications. Measuring blood pressure is a simple and non-invasive way to monitor your health and detect hypertension early on. Blood pressure measuring machines, also known as sphygmomanometers, are widely used to measure blood pressure and monitor hypertension. In this article, we will examine the science behind blood pressure measurement and explore how a blood pressure measuring machine works.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as two numbers. The first number, known as systolic blood pressure, represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats and pumps blood. The second number, known as diastolic blood pressure, represents the pressure in the arteries between beats when the heart is resting. Normal blood pressure is typically considered to be a systolic pressure of less than 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of less than 80 mmHg. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is defined as a systolic pressure of 130 mmHg or higher, or a diastolic pressure of 80 mmHg or higher.
The basic principle behind blood pressure measurement is to determine the pressure in the arteries by occluding the flow of blood. Blood pressure measurement is accomplished by using a blood pressure cuff, which is placed around the upper arm, and a mercury manometer, which is used to measure the pressure in the cuff. The blood pressure cuff is inflated to a pressure that is higher than the systolic blood pressure, and then the pressure is gradually released. As the pressure in the cuff decreases, the first sound that is heard is the systolic blood pressure, and the last sound heard is the diastolic blood pressure.
Blood pressure measuring machines have become much more sophisticated over the years, and modern machines use electronic sensors to measure blood pressure. These machines work by inflating the blood pressure cuff and using an electronic sensor to measure the pressure in the cuff. The electronic sensor sends signals to a microprocessor, which calculates the systolic and diastolic blood pressure based on the pressure readings. The results are then displayed on the machine's digital display.
One of the key advantages of using a blood pressure measuring machine is that it is much more convenient and accurate than manual methods. Blood pressure measuring machines are easy to use and can provide quick and accurate results, making it possible to monitor blood pressure at home or in a doctor's office. Additionally, electronic blood pressure machines can store multiple readings and provide an average of several readings, which can help to provide a more accurate picture of your blood pressure over time.
In conclusion, blood pressure measuring machines are an important tool for monitoring and managing hypertension. By measuring the pressure in the arteries, these machines provide important information about the function of the heart and circulatory system and help to detect hypertension early on. Whether you are monitoring your blood pressure at home or in a doctor's office, it is important to use a reliable and accurate blood pressure measuring machine to ensure that you are getting accurate and useful results. With the right tools and regular monitoring, you can take control of your blood pressure and maintain good health for years to come.