How do Scientists Study the Effects of Pollution on Wildlife?
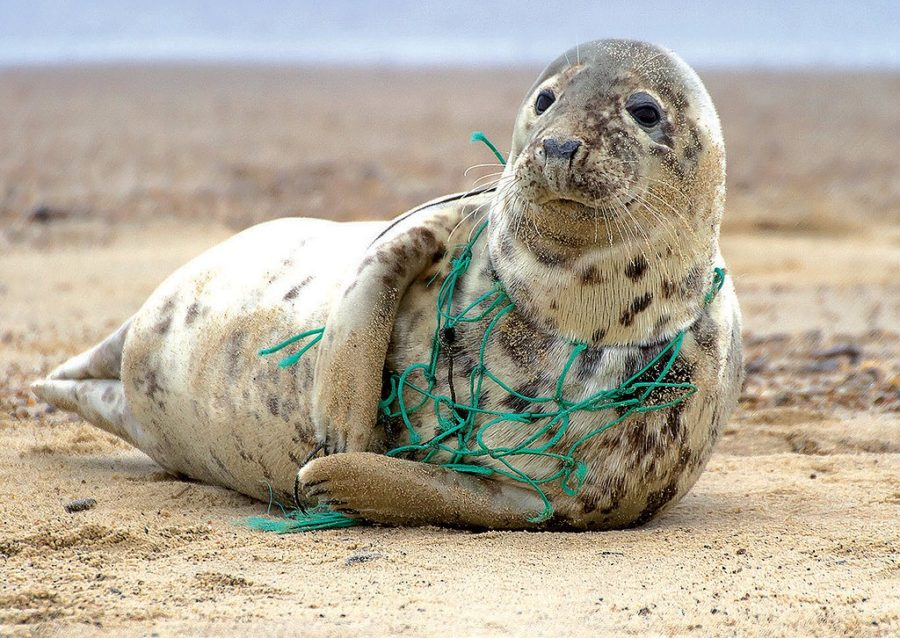
Studying the effects of pollution on wildlife is a crucial area of research for scientists as pollution can have a significant impact on the health and survival of animals. Pollution can take many forms, including chemical, biological, and physical pollution, and scientists use a variety of methods to study the effects of these different types of pollution on wildlife.
One of the most common methods used to study the effects of pollution on wildlife is observational studies. Scientists observe animals in the wild and document their behavior, health, and survival. By comparing the health and survival of animals living in polluted areas to those living in non-polluted areas, scientists can identify the effects of pollution on wildlife.
Another method used to study the effects of pollution on wildlife is experimental studies. Scientists expose animals to controlled levels of pollution in laboratory settings and then observe the effects on their health and behavior. This allows scientists to identify cause-and-effect relationships and make inferences about the effects of pollution on wildlife.
A third method used to study the effects of pollution on wildlife is bioaccumulation studies. Scientists study how pollutants accumulate in the bodies of animals and the potential impacts on their health. This can include analyzing tissue samples and measuring the concentration of pollutants in an animal's blood or fat.
Scientists also use techniques such as remote sensing, GIS and spatial analysis to study the effects of pollution on wildlife by mapping and analyzing the distribution of pollutants and the presence of wildlife in an area.
In addition, scientists use phylogenetic comparative methods and evolutionary approaches to study the effects of pollution on wildlife across different species and over time. This allows scientists to understand how different species are affected by pollution, and how the effects of pollution on wildlife have evolved over time.
In conclusion, scientists use a variety of methods to study the effects of pollution on wildlife, including observational studies, experimental studies, bioaccumulation studies, remote sensing, GIS, and evolutionary approaches. By using these methods, scientists can gain a better understanding of the effects of pollution on wildlife and how these effects have evolved over time. This knowledge can be used to develop conservation strategies to protect wildlife from the negative impacts of pollution.